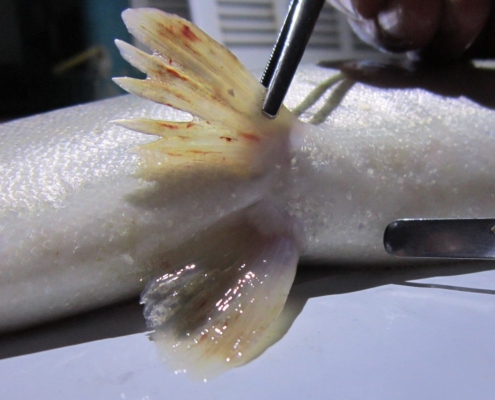
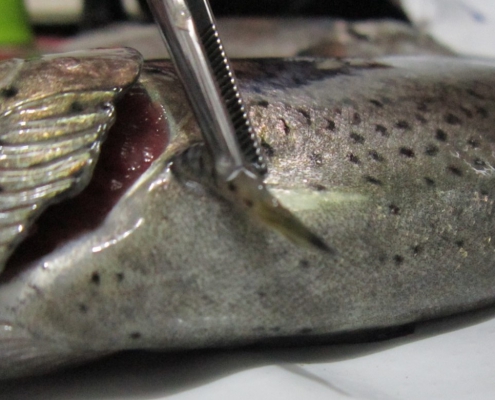
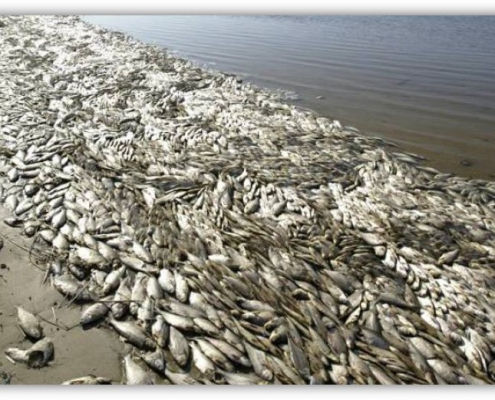
What is the disease?
- Any phenomenon that causes anomalies and defects within a particular population.
- An anomalous phenomenon that is caused by the detrimental effects of living things on fish outside of normal conditions is called disease.
different kinds of diseases
Nutrition
- Atverdisman or Tommel
- Blue glaze of fish
- Lipoidosis
- Hepatoma
- Botulism
- rickets
Atverdisman or Tommel
The disease is caused by a deficiency of vitamin B1 (thiamine) or the presence of thiamine enzyme that causes the vitamin to not be absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. The long axis itself rotates. It should be noted that thiamine is present in the body of fish such as Kilka fish, which is destroyed by heat.
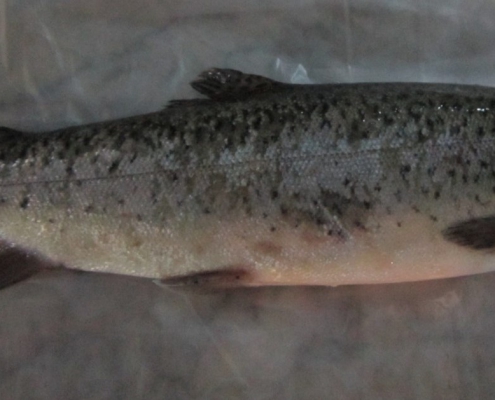
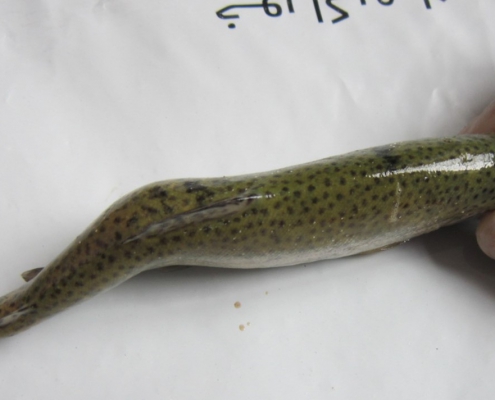
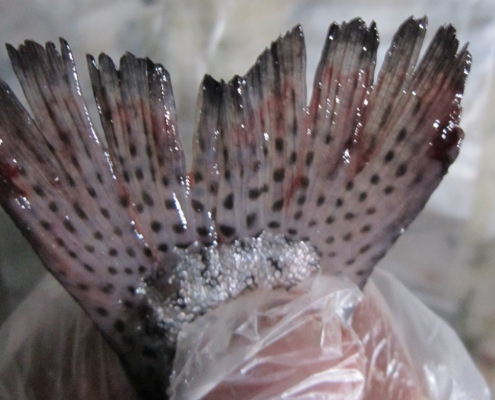
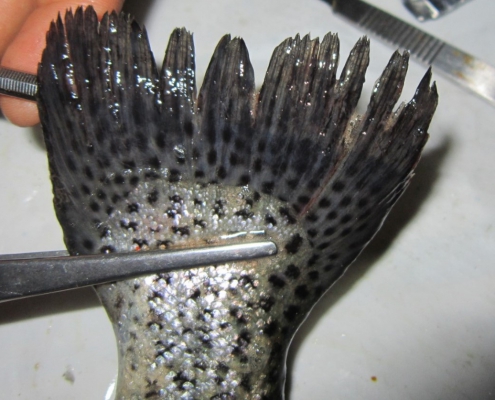
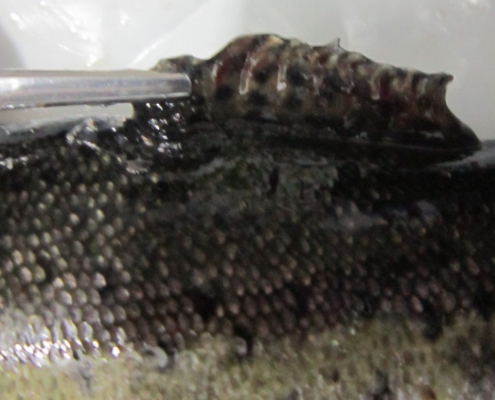
Blue glaze of fish
The blue glaze of fish or biotin deficiency, which forms a bluish-mucous layer, can cover a large part of the fish’s body, which in the course of the layer’s development is lost and gives a speckled appearance to the fish.
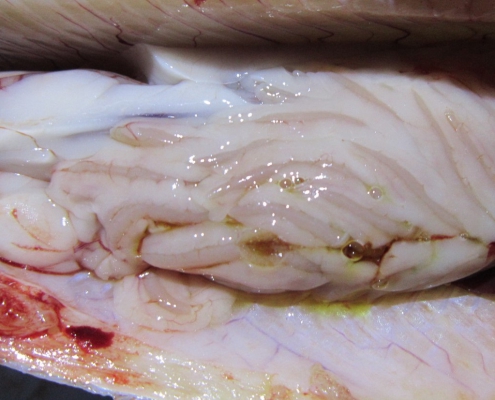
Lipoidosis
Lipidosis or degeneration of the liver fat, which is due to high levels of carbohydrates or fat in the diet, especially in the cold season, and as a result, diet imbalance is the main cause of this complication. Also deficiency of retinol, choline and biotin diet may lead to this complication. It can be cured by modifying the diet and adding vitamin E and increasing fish activity. Symptoms: Color darkness, exophthalmia, fish remain permanently on the surface of the water. The liver is swollen and paleness is evident. The color of the gills changes from dark red to pale red.
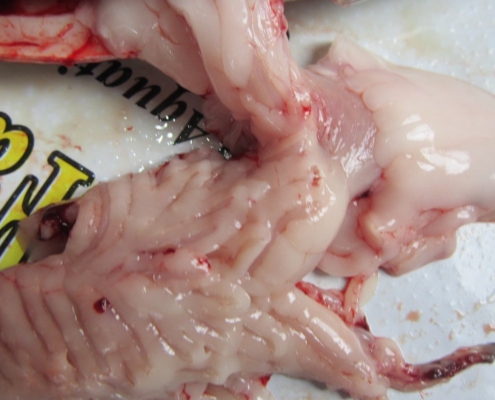
Hepatoma or Aflatoxicosis
Large tumors in the liver, especially in the rainbow trout liver, usually indicate aflatoxin poisoning. Liver tumors appear several months after salmon are fed with even a small amount of moldy oilseeds. Symptoms: Abdominal swelling, anemia caused by a decrease in red blood cell counts, blood protein levels lower than normal, and a slight liver hemorrhage.
Prevention: Keeping food in a cool, dry place and preventing food from molding.
Botulism
The cause of this disease is toxins from a bacterium called CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM.
This bacterium is found in the form of spores in the soil, sludge and intestines of trout grown in the soil pool, which may begin to germinate under heat and lack of oxygen or when fish (dead) in the water. Produce deadly botulonium toxin.
Prevention: Avoid consuming leftover food and spoiled fish and collecting lost fish as soon as possible in pools and eliminating infected fish.
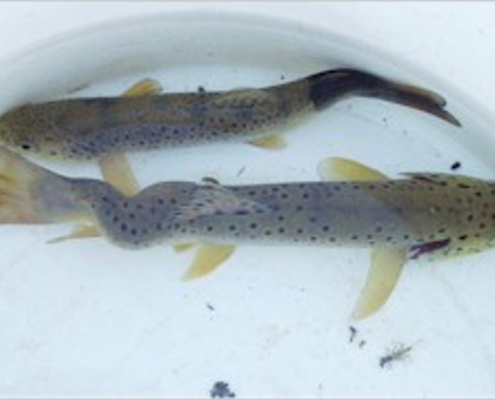
RACHITISME bone softness
Bone tenderness or spine deflection, which is also associated with shortening of the gill cap, may be due to the unbalanced amount of phosphorus and calcium in the fish diet as well as hormonal (pituitary) factors – parasitic infection (Ictosporidium-myxosoma) -microbial (TB) or Inheritance (malformations).
Vertical lordosis spine changes
Spinal changes horizontally scoliosis
Environmental
Environmental Disease:
Sun burn
The disease is caused by the sun’s ultraviolet radiation on the body of the fish, in which case, initially, a distinct stain is created beneath the fish’s skin, and at the advanced stage of the disease, the underlying membrane appears clear, even to the underlying muscles.
Vitamin Niacin deficiency, b and c can increase the sensitivity of fish skin to light.
- GBD gas bubble
The disease, also known as Decompression Sicknes, is caused by an imbalance between soluble gases in the blood (oxygen, Co2, and nitrogen) and the aquatic environment.
The sudden decrease in the amount of these gases in the aquatic environment due to fish blood causes the gases to dissolve and appear as gas bubbles around the eyes and under the fins of the swim, under the jaw and other parts.
Bacterial
Types of Bacterial Disease
- Forced
- Optional: The following are optional bacteria
Flexibactercolumnaris
This bacterium causes Colonaria (hot water disease). This bacterium appears on the microscope slides as columns.
Clinical symptoms
Gray wounds on the fins, which are yellow when the wound is enlarged by bacterial aggregation.
Mucus thickens. The dorsal and caudal fins rot
Damage to the gill tissue appears as bright spots on the head of the gill radius
Cytophagat psychrophilus
This bacterium can cause tail stem rot or cold water disease in salmon.
signs
In the early stages, the edges of the fins rot.
In advanced stages the radius of the fins begin to detach and eventually the tail fin is completely destroyed.
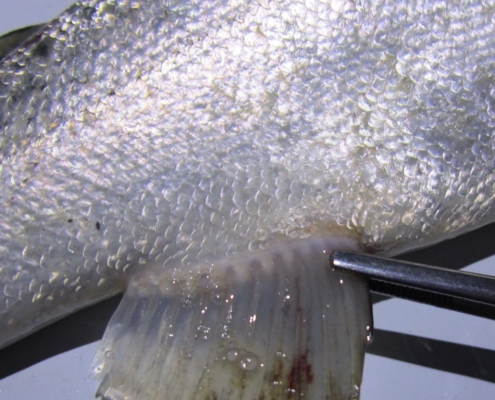
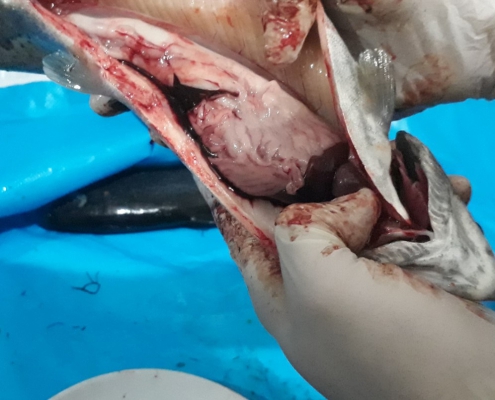
Bacterial Kidney Disease (DKB)
The causative agent of the disease is Rheumatic bacterium Salmonella narum.
It enters the fish’s body through the mouth and through damaged eggs and skin.
Signs
Body color blackness, abdominal swelling, exophthalmia, grayish white abscesses under the skin leading to open sores, kidney, liver and spleen ulcers; fish in areas of the pool that flow more slowly Swimming.
*پیشگیری: مدیریت صحیح، محدود کردن ترددها
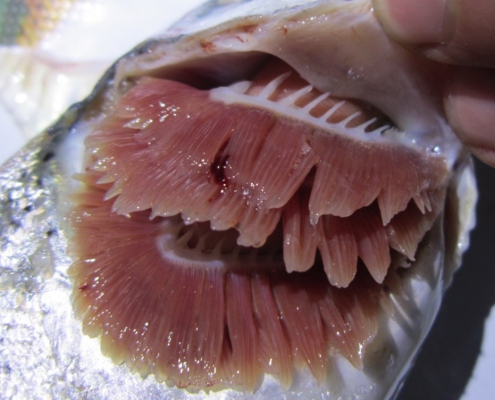
Bacterial gill disease
Cause: High concentrations of ammonia nitrogen (NH3) cause this disease.
Its causes include overfishing, slow water flow, accumulation of bacteria and over feeding.
Forunculosis
The causative agent of this disease is a systemic bacterium called Aero monas salmonidae.
* Severe fatalities occur at the temperature of 14-13.
Signs
There are red spots and inflammation on the skin.
* Prevention: Vaccination, quarantine, restrictions on traffic, restrictions on fish movement
Fungus
-
- Saprolinosis
- Saprolinosis is a term often used to describe fungal infections of the skin and gills. This fungus, by its mechanism of action, causes damage and spoilage in fish skin and on the skin and fins of hyphae or fibers that are usually colored. White can be seen. When the sludge or mud pool is in bed, the color of the hyphae turns into the colors mentioned above.
- Prevention: Fungal diseases should be strengthened against the secondary, including (proper nutrition measures and decreasing density and increasing water quality).
Parasitic
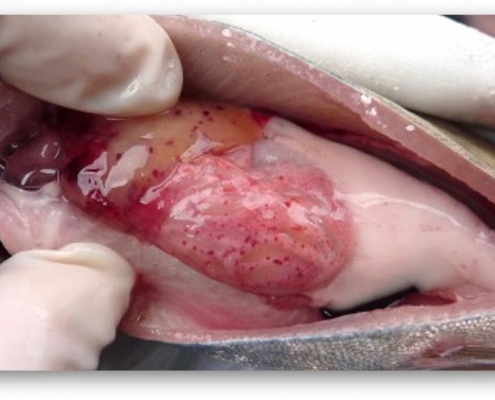
Ichthyophthirius
Appearance Symptoms
* The fish have a short swim and then stop.
* Fish tend not to eat.
* The fins of the fish are seen as sleeping
* The gills secrete a large amount of mucus.
* Bleeding occurs in different parts of the skin
* It hides its fish behind obstacles in the water .
* The fish constantly lures itself around .
* The fish stays on the water and swallows the air .
* Before dying it turns dark gray.
Three biological stages of life: (Active Fertility or White Spot)
The skin stage, the real parasite stage
Relaxation stage, casting stage
Spray stage
Hex Mitosis or Ecto Mitosis:
It affects young trout, especially baby fish. The parasite is the causative agent of hexa-mite Troute or hexa-mitasalmonis that appears in the intestine of fish. Appearance Symptoms: Fish tend to be abnormal and have poor appetite. In the autopsy, a portion of the intestine immediately after the stomach contains a bright yellow liquid.
Treatment: Medications such as Omtril, Di Metronidazole, or Flagella with food.
Dactylogyrus:
Its size is up to about 1 mm, producing white and triangular eggs. And the parasite is a specialized gill-free fish that transmits directly from one fish to another. This parasite destroys its gill tissues with its gloves and hooks.
Argulus or fish louse:
شپشک ماهی یک سخت پوست کوچک است که دارای بدنی پهن و گرد و شفاف به رنگ سبز کم رنگ و 4 جفت پای شناگر می باشد.
Symptoms: Argulus attaches to the body of the fish, causing itching of the fish and forcing it to rub on the body.
Argulus is a small hard skin that has a broad, round, translucent body in pale green and four pairs of swimming legs.
The bite of this parasite causes secondary infections such as infectious flooding and saproligenia in fish.
Diplostomiasis
It is caused by the Diplostomum parasite. The adult diploid parasite is flat and flat.
Life Cycle: The adult parasite is found in the intestine of the fish eater, the host of which is the intermediate lemongrass snail and the host of the second intermediate is most often the fish that is housed in the lens of the eyeball.
Symptoms: White spots (cataracts) on pupil black background
Whirling Disease
The cause of this disease is the parasite myxozoma cerberalis. The parasite spores enter the free skull cartilage of fish less than six months of age and cause a severe reaction in the fish when the skull becomes bony or the length of the fish reaches 6 to 8 cm.
Symptoms: The fish will rotate around, deforming the back and tail and becoming darker, with symptoms occurring after 40 to 60 days.
Prevention: Use contaminated water and disinfectants to clean pools and equipment.
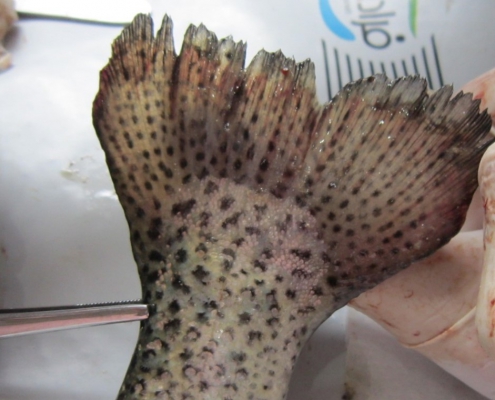
lernaea or anchor worm
This is a parasite of crustaceans. The causative agent in this parasite is the female genus, which engulfs its contents into the fish’s skin and muscles and stabilizes them there.
The host’s body becomes inflamed by the parasite’s head, and parasites that cling to the jaw and mouth of the fish cause the fish to eat and become extremely weak.
Gyrodactylus
This parasite is one of the widespread kernels and is a specialized skin parasite.
It is also a living parasite. Sometimes it infects fish skin and eyes.
They often focus on the back and tail.
Viral
A variety of viral diseases
Viral hemorrhagic septicemia(VHS)
Red mouth disease
Infectious necrosis of hematopoietic tissue (IHN)
- Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis (IPN)
VHS: Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia
The disease is found in salmonids below 8 degrees Celsius
Transportation Ways:
Birds, animals
signs:
Exophthalmia, hemorrhage around the eyes, pale gills, intense swimming, thin and red kidneys, most deaths are seen in fish up to 200 g.
Infectious necrosis of hematopoietic tissue (IHN):
The disease is most commonly seen in trout less than 2 months old
Transportation Ways:
Direct contact of infected fish with healthy fish, eating carcass of infected fish, by water, from broods hatched to infants
signs:
Comet Stool exit, Exophthalmia, Pale Gills, Abdominal Dilatation
Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis (IPN):
Infecting Pancreatic Necrosis
The disease infects young trout more:
Signs:
- The sudden rise of casualties
- Darkening of body color
- Eye protrusion
- Bleeding in the pancreas
- Bleeding in the stomach
* Final diagnosis is possible by isolating the virus from the intestine or genitals.
Ichthyophthirius
ichthyophthiriusmultifiliis (ic parasite(
Three biological stages of life
- Spray stage
- Relaxation stage, casting stage
- The skin stage, the real parasite stage
Parasite Ick – Appearance Symptoms
The fish have a short swim and then stop.
- Fish tend not to eat.
- The fins of the fish are seen as sleeping
- The gills secrete a large amount of mucus.
- Bleeding occurs in different parts of the skin.
- It hides its fish behind obstacles in the water.
- The fish constantly lures itself around.
- The fish stays on the water and swallows the air.
- Before dying it turns dark gray.
Carassiusauratus
- These include flatworms and it is a specialized skin parasites.
- Biogenic (Live bearers)
- Skin and eyes
- They often focus on the back and tail
Trichodina parasite
- Swims easily in water
- Looking for a host to continue living.
- If symptoms occur in a fish, most of the fish in that parasite usually become infected.
- Poor water quality exacerbates the disease process.
Live food and contaminated fish are the main reasons for this parasite to - enter the pool
- Scratching and slapping body skin on objects in the pool
- Darkening of body color
- Stay idle or get stuck
- The appearance of white spots and spots on the skin surface
- Cloudy eyes
- Coming to the surface of the water and breathing heavy, irregular and irregular to catch oxygen (if gills become infected)
- The patchy white layer on the tuna
- Mucus secretion on the surface of fish to protect the skin
- Lack of appetite
- loose weight
- Loose and go into a state like sleep or coma !!! And finally death