Recirculating Aquaculture Breeding – Step Four
Biological purification
not all particulate matter and waste are removed in a mechanical filter, some of the particles pass through it as soluble compounds such as phosphate and nitrogen. Phosphate is an inert substance, with no toxic effect, but nitrogen is toxic to free ammonia, and must be converted to harmless nitrate. Decomposition of organic matter and ammonia is a biological process performed by bacteria. Heterotrophic bacteria produce organic matter by consuming oxygen and producing carbon dioxide, ammonium and nitrite. Bacteria convert ammonia to nitrite and eventually to nitrate.
Two things are very important in this way:
A) water temperature in the system B) pH level in the system
To achieve an acceptable rate of nitrogen fixation, the water temperature must be maintained at 10 to 35 ° C (about 20 to 30 ° C) and pH between 7 and 8. The water temperature often depends on these and is not set to reach the maximum nitrogen fixation rate, but to achieve optimum levels of fish growth to reach optimum temperature levels. Adjusting the pH with respect to bio-filter efficiency is important because lower pH levels reduce productivity. Therefore, the pH must be maintained above 7 to achieve a high level of bacterial nitrogenation. On the other hand, increasing the pH leads to an increase in the amount of free ammonia NH3 which will increase the toxic effect. So the goal is to find a balance between the two goals of adjusting pH and temperature. A suggested set point is between pH seven and pH seven and a half.
Two main factors affect the pH of the water circulation system:
A) Co2 production from fish and biological activity of biological filter B) Acid produced by nitrogen fixation process
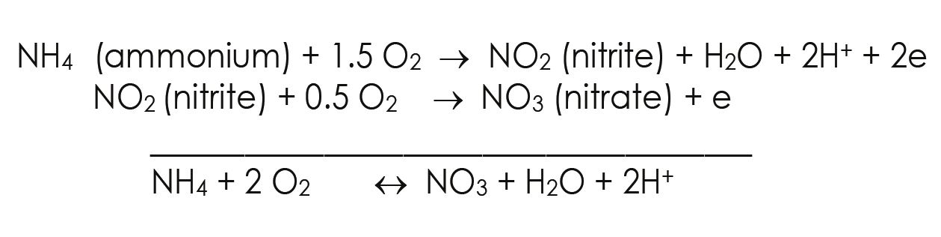
CO2 is excreted by aeration of water, whereby degassing occurs. This process can be done in a variety of ways, which will be explained later in this section.
The nitrifying process produces acid (+ H) and the pH level decreases. A base must be added to stabilize the pH. For this purpose, sodium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or another base must be added to the water.
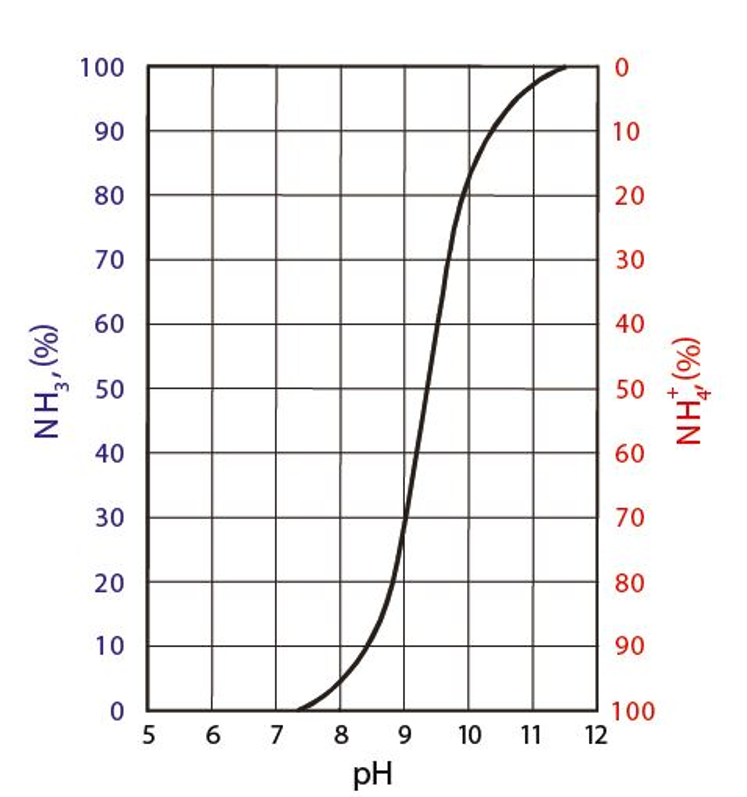
Ammonia is a mixture of ammonia and ammonium (Total) = ammonium (NH4 +) + ammonia (NH3) in which ammonia forms the major part of the waste. But the amount of ammonia in water depends on the table:
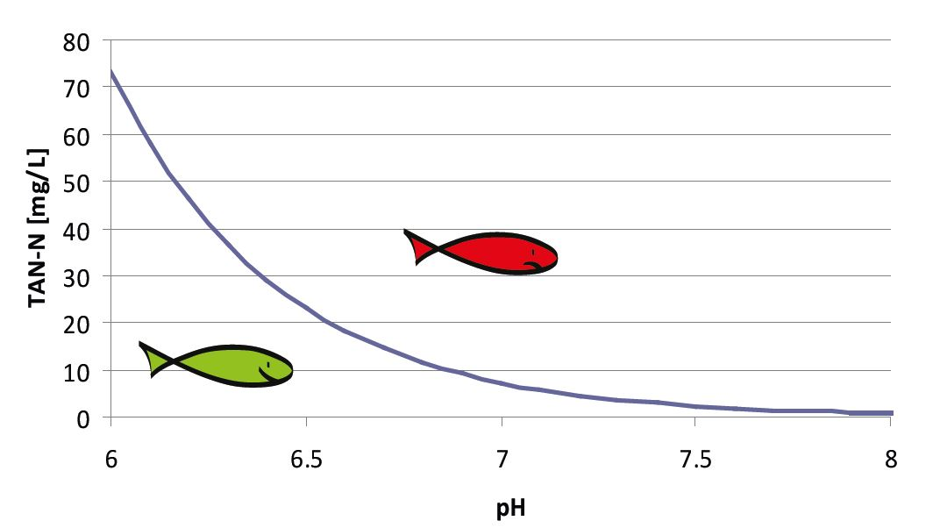
In this picture you can see the equilibrium between ammonia (NH3) and ammonium (NH4 +) at 0 ° C. No toxic ammonia is present at low pH but increases with increasing pH. The pH level can be detected in the figure, which shows the equilibrium between ammonia (NH3 +) and ammonium (NH4 +). In general, toxic ammonia is toxic to fish at more than 0.02 mg / L. The following figure shows the maximum concentration of toxic ammonia, which is permissible at different pH levels if a level below 0.02 mg / L is guaranteed. A lower pH level reduces the risk of exceeding the permissible level of ammonia by 0.02 mg / L, but the fisheries manager is advised to reach a level below the minimum pH of 7 to achieve bio-filtering.
The table above is the relationship between the measured pH and the amount of TAN available for biodegradability, based on the toxic ammonia concentration of 0.02 mg / L.
Nitrogen (nitrogen dioxide) is formed in the intermediate stage in the nitrogen fixation process and is toxic to fish at levels above 2 L / mg. If the fish breathe in a circulatory system, although oxygen levels are good, high nitrite concentrations may be the cause. At high concentrations, nitrite is transported through the gills into the fish’s bloodstream, preventing oxygen uptake. By adding salt to water, it absorbs up to 0.3%, inhibiting nitrite uptake.
Nitrate is an end product in the nitrogen fixation process, and although considered high levels (above 20 to 50 mg / L) have a negative impact on food growth and conversion. If the new water exchange is kept in the system too low, the nitrate will accumulate and the results will be unacceptable. One way to prevent nitrate accumulation is by increasing the exchange of new water, where high concentrations are diluted to a low level without hassle.
n the other hand, the whole idea of Recirculating Aquaculture Breeding is fish storage, and in some cases water saving is a big goal. Under such conditions, the nitrate concentration can be reduced to nitrogen uptake. Under normal conditions, water consumption of more than 300 liters per kilogram of feed used is sufficient to dilute the nitrate concentration.
Most of the dominant bacteria are called pseudomonas. This is an anaerobic process (without oxygen) to reduce nitrate to atmospheric nitrogen. In fact, this process separates nitrogen from water into the atmosphere, where the nitrogen load is reduced to the surrounding environment. This process requires an organic source (carbon), for example wood alcohol (methanol), which can be added to the nitrate chamber. In practical terms, 2.5 kg of methanol is required for each kg of nitrite (NO – N) denitrified.
Most nitrate decontamination rooms are equipped with bio film or special surfaces designed with a 2 to 4 hour residence time. The flow must be controlled to keep the oxygen concentration of the output in the program. If oxygen is produced more than one milligram per liter, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) will occur, which is highly toxic to fish and also has a nasty smell (rotten eggs). In the process of nitrating, the obtained sludge production is very high, and the nitrate removal unit should be washed once a week.
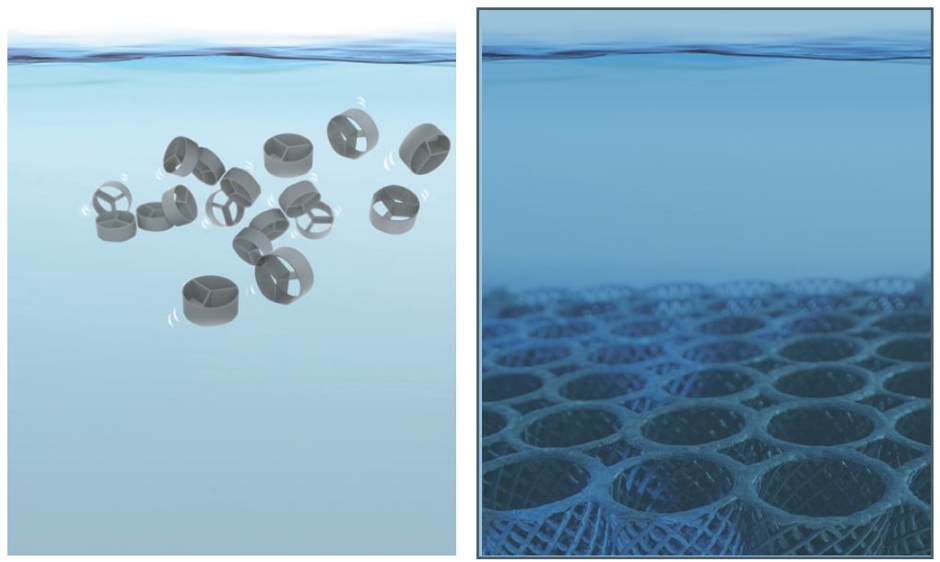
Examples of bio-films for use in bio-filters:
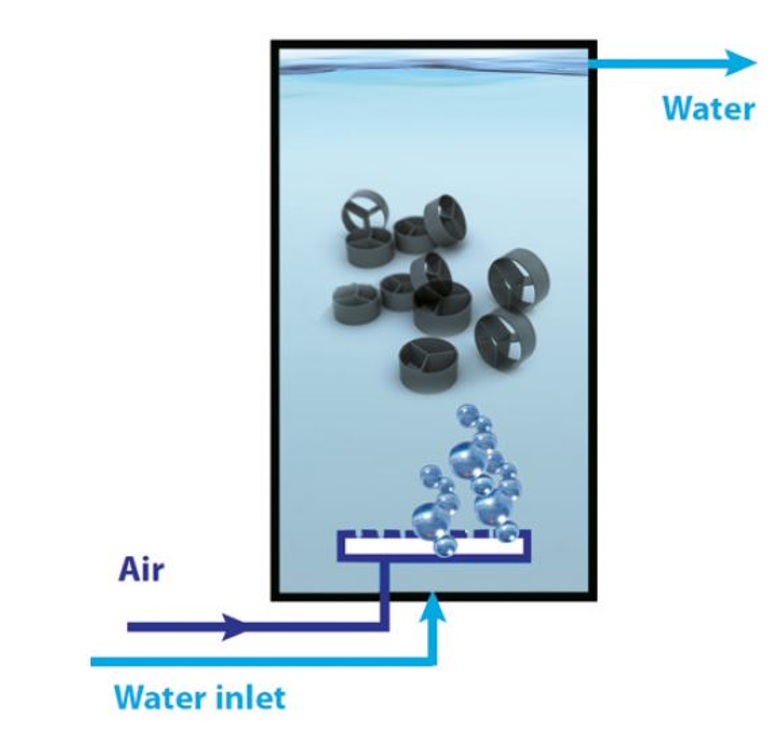
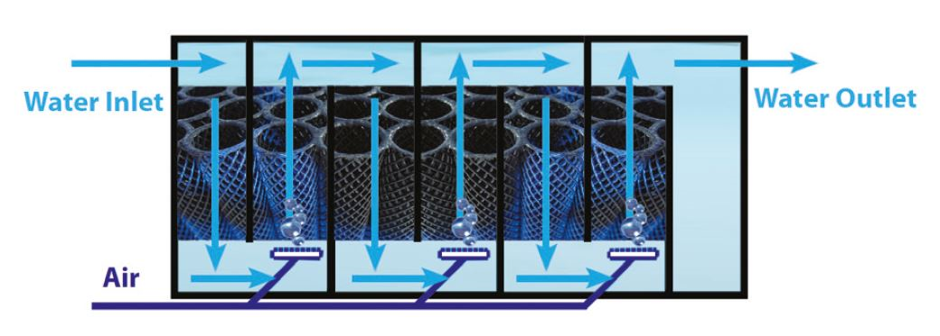
Bio-filters are usually made using plastic media that give a high level per cubic meter. The bacterium will grow as a thin layer on the media, thus occupying a very large surface. The purpose of a well-designed bio-filter is to achieve a high level per cubic meter without clogging with organic matter. Therefore, it is important to have a high percentage of free space for water to pass through the bio-filter and to have a good overall flow with adequate washing. Such steps should be performed at intervals of three weeks or one month depending on the load on the bio-filter. Compressed air is used to create a continuous flow in a filter in which the organic matter is removed. As the washing process occurs, it will be cleaned and the dirty water discharged into the filter and discharged before it can be reconnected.
Design flat bed filters or removable bed filters. All bio filters used in closed circuit farms today act as submerged units. In a fixed flat filter, the plastic media is stationary and does not move. Water flows through the media as a quiet stream to communicate with film bio. In the removable bed filter, the plastic media moves through the water with the flow created by the air pump. Due to the constant movement of media, removable bed filters can be harder than fixed bed filters, resulting in higher displacement rates per cubic meter. However, there is no significant difference in the calculated turnover rate per square meter (filter surface area) as the bacterial film bioassay efficiency in either.
Examples of bio-films for use in bio-filters:
Bio-filters are usually made using plastic media that give a high level per cubic meter. The bacterium will grow as a thin layer on the media, thus occupying a very large surface. The purpose of a well-designed bio-filter is to achieve a high level per cubic meter without clogging with organic matter. Therefore, it is important to have a high percentage of free space for water to pass through the bio-filter and to have a good overall flow with adequate washing. Such steps should be performed at intervals of three weeks or one month depending on the load on the bio-filter. Compressed air is used to create a continuous flow in a filter in which the organic matter is removed. As the washing process occurs, it will be cleaned and the dirty water discharged into the filter and discharged before it can be reconnected.
Design flat bed filters or removable bed filters. All bio filters used in closed circuit farms today act as submerged units. In a fixed flat filter, the plastic media is stationary and does not move. Water flows through the media as a quiet stream to communicate with film bio. In the removable bed filter, the plastic media moves through the water with the flow created by the air pump. Due to the constant movement of media, removable bed filters can be harder than fixed bed filters, resulting in higher displacement rates per cubic meter. However, there is no significant difference in the calculated turnover rate per square meter (filter surface area) as the bacterial film bioassay efficiency in either.
There are also different types of filters. However, in fixed bed filters, organic particles are also removed well because they are attached to the film bioassay. Therefore, the flat bed filter also acts as a good mechanical purification unit that destroys microscopic organic matter and makes the water very transparent. The removable bed filter will not have the same effect because the constant turbulence of the water does not have the proper adhesion.
Both filter systems can be used in the farming system, or can be combined, using a removable litter for space saving and a fixed litter for double effect. There are several solutions in the individual fisheries department for the final design of bio-filter systems that are designed based on farm size, species of fish for cultivation, size and size of fish etc.
Behruz Alinia Fard
Fisheries Analyst and Complicator