Sturgeon reproduction
Sturgeon are a group of laying fish and eggs and sperm are floated in the water and fertilization is done at random. These fish do not care for their children. sturgeons (Life Cycle 3) migrate to freshwater rivers for spawning, and the rivers they choose are often muddy, relatively deep and with a strong flow, sturgeon eggs to bushes and leaves in water or to rocks The bottom of the river adheres, and as the water flows through it, the incubation process becomes larvae. After 2 to 6 months of staying in the river, baby fish will be seaward. Male fish reach sexual maturity earlier than female fish. The age of pestilence varies in different species as well as different places of life:
| Gender | Starry sturgeon | Persian sturgeon | Beluga |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ۷-۵ | ۹-۸ | ۱۴-۱۲ |
| Female | ۱۲-۱۰ | ۱۴-۱۰ | ۱۸-۱۶ |
Given that the sturgeon is sexually mature in five stages, so distinguishing these stages from either artificial breeding of wild-caught broodstock aimed at producing baby fish to rebuild stocks or artificial breeding and baby fish production at farming sites. Meat, and most importantly, caviar extraction from reared fish is very important.
On the other hand, because of the longer puberty age of sturgeon than other fish, due to the high value of caviar female breeders are much more valuable than male breeders, and maintenance and breeding of males is not affordable at all. The sexual maturity stages of the sturgeon are divided into five stages, as follows:
Step One Of Sexual Maturity:
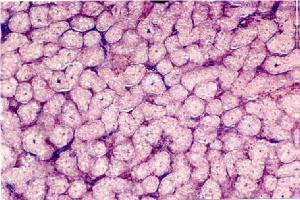
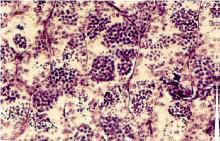
Macroscopically they are white stripes in both sexes and cannot be detected by observation. In microscopy and tissue preparation, the ovarian fissures are separated by division, and the appearance of the ovogenic cells has begun. The primary eggs are small and each are 50 microns in diameter and comprise a large nucleus of bacromatin. In stage 1 sexual maturation in the gonads of the transplanted tissue and the large blood vessels formed by spermatogonial cells. The thin layer of connective tissue is a prominent feature of the initiation of male sex glands.
Step Two Of Sexual Maturity:
In females: The diameter of 1 oocyte reaches about 100 to 250 microns. Significant signs of this stage include covering of fat deposits in the abdomen and lateral parts of the ovary and cystic plasmic growth of the oocytes. The duration of this period is very long and depends on the external conditions of the living environment.
Stage 2 in the male: The embryonic portion of the testis is enlarged (approximately 1.3 gland volume) and contains differentiated cysts that contain primary spermatocytes. In the male sex this is the longest stage. Macroscopically, stage 2 is layered in sex, but is observed in male testicular tissue.
Step Three Sexual Maturity:
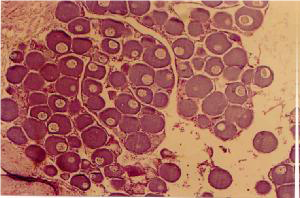
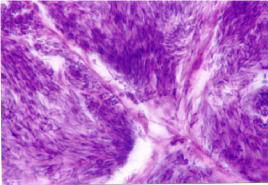
Stage 3 Macroscopically, the female is red and orange. The difference of this stage from the two is quite noticeable. The eggs are clearly differentiated and the nucleus and micropyle are clearly visible. The adipose tissue is reduced and the pigments are gray. In stage 3, the male sperm are rounded, needle-shaped and white. Primary, secondary spermatocytes and their divisions are formed.
Step Four Sexual Maturity:
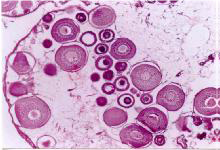
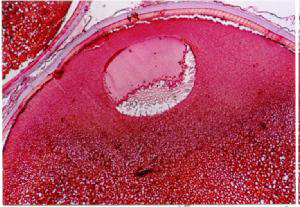
Stage 4 can be distinguished in the sexes of the plant and animal poles. At this point, the nucleus shifts from the center of the cell to the animal pole. The fine-grained yolk is concentrated in the animal pole and the coarse-grained yolk with the fat droplets in the plant pole. The germ cell is called the germinal vesicle. It has a large number of nucleus with a fully developed wall. This stage itself consists of 3 parts of the A.B.C.
Stage B is the best time for caviar and hormone injection to induce ovulation. GV coefficient is calculated by the time of hormone injection and the induction of sexual maturation. Stage 4 in the male: The sex cells are not overweight but are more elongated. Large, white testicles are seen throughout the cavity or for mature spermatozoids. The stage of egg and sperm excretion is called stage V. After this stage, she re-enters Stage 2, which is one of the diagnostic methods that the productive spawns several times since Stage 1 is no longer observed after the first spawning and enters Stage 2 directly.
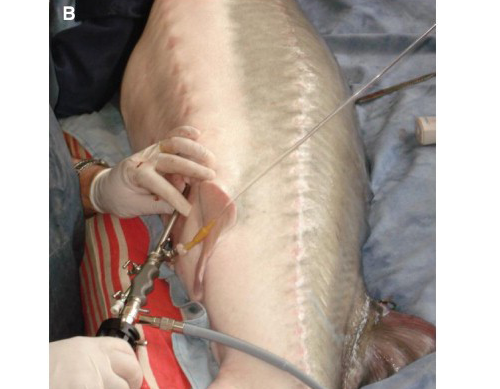
In many species, male and female fish are easily distinguishable from each other due to their secondary sexual characteristics. This is less common in pre-adolescence and especially in fish that were not in the natural environment and at sea. For this purpose, different methods are used to diagnose these steps, based on the method of operation, such as invasive procedures such as blood sampling, biochemical diagnostics, low invasive procedures such as laparoscopy, biopsy, and non-invasive procedures such as ultrasonography and morphology.

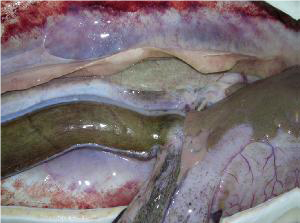
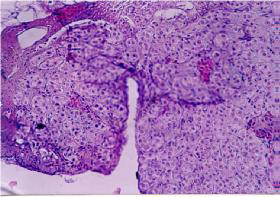 Macroscopic observation at stage I
Macroscopic observation at stage I