Recirculating Aquaculture Breeding – Step Five
Degassing, aeration and water rotation:
Accumulated gases that are harmful to fish must be removed before returning water to the fish tank. This degassing process is performed by water aeration and this method is often referred to as degassing. Water contains carbon dioxide (CO2) from fish respiration and from bacteria in biological treatment at the highest concentration, but there is also free nitrogen (N2). The accumulation of carbon dioxide and the amount of nitrogen gas will have a detrimental effect on the comfort and growth of fish. Under anaerobic conditions, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) can be produced especially in saline water systems. This gas is very toxic to fish, even at low concentrations, and if the hydrogen sulfide is produced in the system, the fish are killed. Aeration can be done in different ways by pumping air into the water.
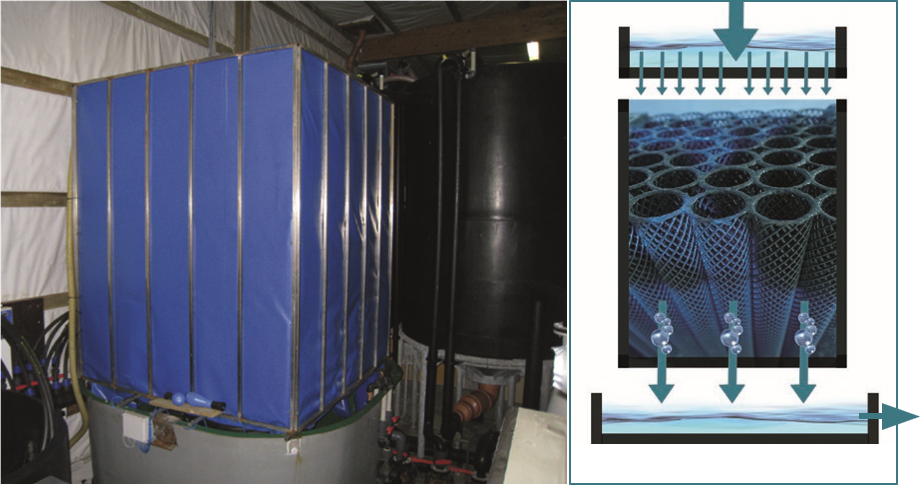
The photo and drawing of the drip filter are designed in a blue plastic line to prevent splashing on the floor. The process of aeration is called degassing or the elimination of harmful gases. A drip filter medium usually contains the same type of media used in a fixed bed.
Turbulent contact between air and water bubbles causes harmful gases to come out of the water. This underwater aeration allows water to flow in the moment, if a good aeration system is used.
However, a good aeration system is not as effective as a drip filter system. In the drip system, gases are removed by physical contact between the water and the plastic media stacked in a column. Water is directed to the top of the filter on a distribution plate with the holes created and flushed through plastic media to maximize turbulence and impact, and so-called discharge down.
Behruz Alinia Fard
Fisheries Analyst and Complicator