Fish farming in Australia
The history of fish farming in Australia dates back to more than a thousand years ago when Australian Indigenous people in West Victoria, now the Bougainvillea National Park, built waterways along the mouth of the river to collect water and trap certain species of eels. This species was naturally bred there and was nourished by Indigenous peoples. Australia has a major role in the aquaculture and fishing industry due to its 25,760,000 km coastline. In fact, fish farming in Australia is done in two ways:
Sea
Fresh water (land)
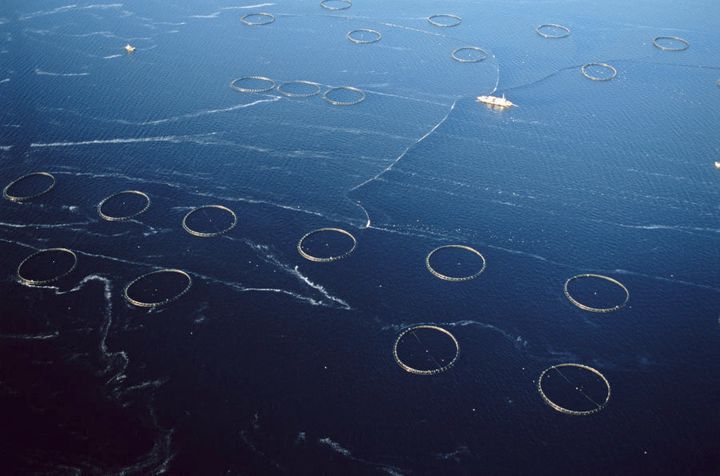
Fish farming in Australia is done in two ways, near the shore and offshore, in special cages and nets. Some manufacturers produce in advanced pools equipped with fresh water. Also, breeding of certain species of aquatic animals is done in the estuaries.
Fish farming is currently one of the major growing industries in Australia, accounting for 40% of the total value of seafood. Commercially bred fish in Australia include bluefin tuna, salmon, trout and yellow-tailed herring, and fish such as sardines, white bites and pilchards are never bred in Australia because they are not domesticated. The production of oysters and pearls is also one of the most profitable products of the Australian fisheries industry.
Breeding ocean trout
Ocean trout are native to the cold waters of the North Atlantic and came to Australia in the 19th century for commercial production. Salmon are currently bred in marine cages in Tasmania. The salmon farming cycle is like the Atlas salmon. The appearance of the ocean trout is similar to that of the rainbow and brown trout, which have large jaws and red and black spots on their bodies. Hunters have a varied diet and eat whatever they catch. The state of Tasmania produces more than 14,000 tons of Atlantic salmon and ocean trout worth more than $ 110 million a year.
Atlantic salmon farming
Atlantic salmon is a member of the Salmonidae family found in the North Atlantic and the rivers that flow north of the ocean. These fish are found in the Pacific Ocean and South Australian waters. Adult salmon feed on adult squid, shrimp, eels and other fish. Salmon is highly valued by fish-eating birds, especially when they migrate to freshwater to breed and feed on food. In Tasmania, salmon are bred en masse in offshore sea cages, but the farmed diet differs from the wild. The diet of farmed salmon mainly consists of small farmed fish and some special plants.
Southern bluefin tuna farming
The southern bluefin tuna industry is currently one of the most lucrative economic sectors in South Australia. This sector exports most of its products, which has led to competition between exporters of tuna (blue tuna, big tuna and yellow tuna). Southern bluefin tuna is the main species bred in Australia. The most important export destination of tuna is Japan, which is the largest consumer of sashimi in the world. Tuna is caught in the southern ocean and transported to Lincoln Harbor and kept in cages for 2 to 3 months to be fed. No antibiotics or chemicals are added to tuna foods. The growth process of fish, their ambient temperature as well as the amount of oxygen they consume are constantly monitored by producers. The tuna diet is a combination of other high-fat fish such as sardines, gypsies, mackerel and squid. Floating nets and traps were installed to maximize the flow of water. Winter months are the best time to harvest tuna because they have reached their desired size in this season.
Breeding yellow-tailed herring
Yellow-tailed herring is found in cold waters such as the Pacific Ocean, India, South Africa, Japan and South Australia. Yellow-tailed herring is a carnivore and feeds on a variety of fish and its average weight is about 4 kg. It is one of the most powerful ocean fish known for its yellow tail. This fish is found in different colors of bright green or blue and glossy black all over the world. Yellow-tailed herring is highly regarded as a farmed fish in Australia and is commercially produced on a large scale.
The most important aquaculture companies in Australia
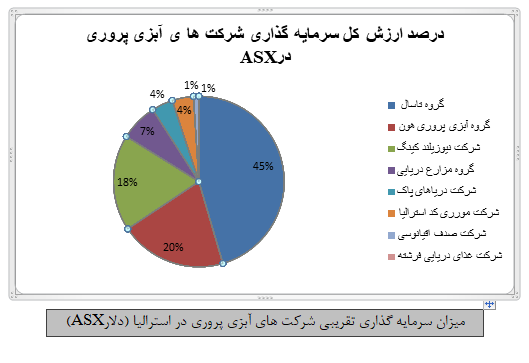
There are currently eight companies active in aquaculture and fish farming in Australia, with Tasal Group having the largest share of the ASX stock market, followed by Hoon Aquaculture Group. The total value of the investment by aquaculture companies in ASX is about $ 2 billion.
Tassal Company
It is one of the largest salmon farming and seafood processing companies in Australia. In 2010 and 2011, it invested nearly $ 200 million in a five-year plan to improve and expand production structures, making Tasal a pioneer in salmon farming and transforming it from a cost-effective firm to a printer. At present, the company exports its products on a large scale.
Huon Aquaculture Group Limited
The company was founded in 1994 and joined ASX in 2014, which is one of the largest salmon farming companies and has recently taken significant steps to develop its products. Hun Tas, like Tasal, has all the tools and facilities to raise fish in Tasmania. In addition, during 2018, Hoon began commercially breeding yellow-tailed herring commercially in Queensland and Western Australia. Seafood processing is one of the most important and profitable parts of Hun Company, which is exported to all over the world.
New Zealand King Company
New Zealand King is one of the largest producers of salmon (one of the quality species of salmon). The company operates 7 farms and earns most of its revenue through exports.
Sea Farms Group
Offshore Company is the largest producer of shrimp in Australia with a capacity of 1800 tons per year. The company sells its products under the Crystal Bay Shrimp brand. The company has been based in Queensland since 1988 and produces several varieties of shrimp. In a project called Dragon, which is a program to expand the company’s activities, advanced production facilities will be established in the northern regions, which will include 10,000 hectares of swimming pools, and will be implemented in several stages.
Clean Seas Limited Company
Clean Seas is a producer of yellow-tailed herring in Lincoln Bay, Spencer Bay, South Australia, which joined ASX in 2005. The company intends to increase its production in the Gulf of Valaro and Arno. In the past, he decided to breed bluefin tuna, which he gave up.
Murray Cod Australia Limited
The company produces the Murray Code fish in the Riverina South Wales region of Australia. The moray eel is a predatory fish that lives in freshwater. This fish has other names such as green fish, cod, godo, Queensland freshwater fish and pound. Murray hunting is illegal because it is one of the most important wildlife species in Australia. So the only way to use this fish is to breed it. Murray Code is a special product and its wholesale price is more expensive per kilogram than other fish. ($ 24-25 per kilogram compared to $ 12-14 salmon). It requires less capital than the lake or ocean model.
Ocean Grown Abalone Company
Is a trading company producing Abolone oysters in Western Australia. There are 11 species of abalone, only 3 of which are large in size and economical. The average weight of each adult abalone is about 250 to 350 grams with a size of 13 to 17 cm. It is one of Australia’s most valuable products in the fisheries industry ($ 100 per kilogram).
Angel Seafood Company
The company is an oyster producer in South Australia. Angel Seafood in the Gulfs of Kafin, Smokey, Kowl and Haslam carry out the production process. It sells its products internally and externally and joined ASX in 2018. The company intends to expand its regional products and expand its position in the global market. Fish farming is one of the most lucrative industries in Australia, with exports projected to increase by 4% to $ 1.68 billion in 2023 and 2024, respectively. Australia’s fisheries sector is heavily dependent on trade and the goal of large producers is to increase their production volume and highlight their role in the global market.